Match the appropriate constitutional convention plan with its features. – The Constitutional Convention of 1787 was a pivotal moment in American history, where delegates from across the newly formed nation gathered to draft a framework for a new government. Among the many plans and proposals presented at the convention, three primary plans emerged: the Virginia Plan, the New Jersey Plan, and the Connecticut Compromise.
These plans reflected different visions for the structure and powers of the new federal government, and their features and impacts played a crucial role in shaping the final Constitution.
In this exploration, we will delve into the key features of each plan, analyze their differences, and examine their lasting impact on the development of the United States Constitution.
Virginia Plan
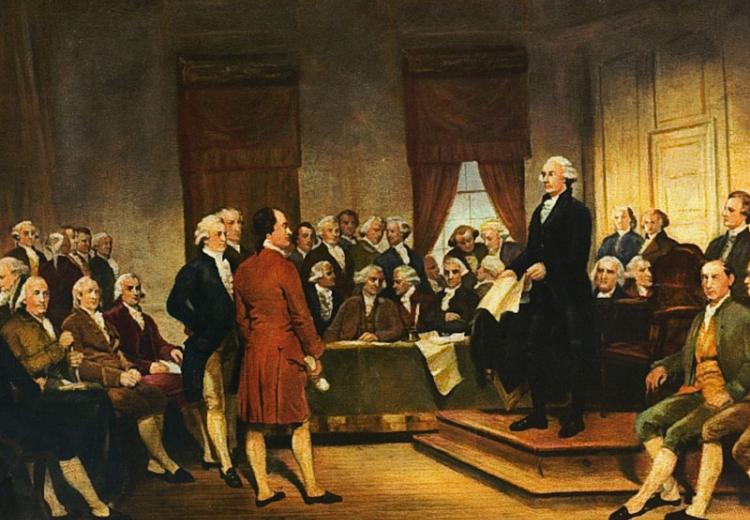

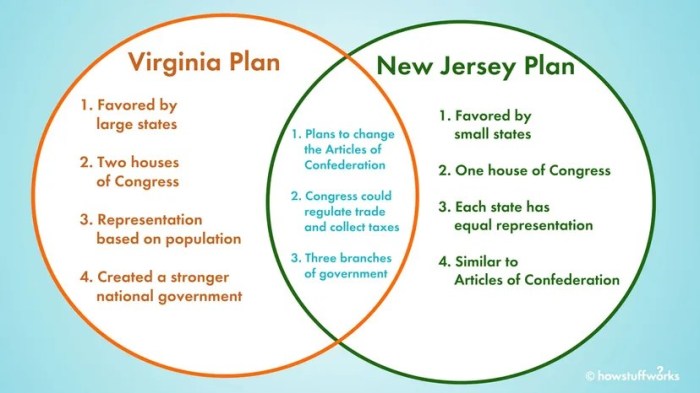
The Virginia Plan, proposed by James Madison, was a comprehensive proposal for a new federal government. It called for a strong central government with three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. The legislative branch would be bicameral, with the upper house (the Senate) representing the states and the lower house (the House of Representatives) representing the people.
The executive branch would be headed by a single president, elected by the legislature. The judicial branch would consist of a Supreme Court and inferior courts, appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate.
Key Features
- Strong central government
- Three branches of government: legislative, executive, and judicial
- Bicameral legislature: Senate representing states, House of Representatives representing the people
- Single executive: president elected by the legislature
- Appointed judiciary
The Virginia Plan had a significant impact on the Constitutional Convention. It provided a framework for the new government and many of its provisions were ultimately adopted into the Constitution.
New Jersey Plan
The New Jersey Plan, proposed by William Paterson, was a more conservative proposal that sought to preserve the power of the states. It called for a unicameral legislature, with each state having one vote. The executive branch would be headed by a council of executives, elected by the legislature.
The judicial branch would consist of a Supreme Court, appointed by the legislature.
Key Features
- Weak central government
- Unicameral legislature: each state with one vote
- Council of executives as the executive branch
- Appointed judiciary
The New Jersey Plan was not as popular as the Virginia Plan and was ultimately rejected by the Constitutional Convention. However, some of its provisions, such as the equal representation of states in the Senate, were incorporated into the final Constitution.
Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise)
The Connecticut Compromise, proposed by Roger Sherman, was a compromise between the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan. It called for a bicameral legislature, with the Senate representing the states and the House of Representatives representing the people. However, the Senate would be elected by the state legislatures, while the House of Representatives would be elected by the people.
Provisions
- Bicameral legislature: Senate representing states, House of Representatives representing the people
- Senate elected by state legislatures
- House of Representatives elected by the people
The Connecticut Compromise was a major turning point in the Constitutional Convention. It resolved the conflict between the large and small states and paved the way for the creation of a new federal government.
Three-Fifths Compromise

The Three-Fifths Compromise was a compromise between the Northern and Southern states on the issue of slavery. It provided that three-fifths of the enslaved population would be counted when determining a state’s population for the purposes of representation in the House of Representatives and taxation.
Impact, Match the appropriate constitutional convention plan with its features.
- Increased the political power of the Southern states
- Delayed the abolition of slavery
The Three-Fifths Compromise was a controversial provision that had a significant impact on the course of American history.
Electoral College
The Electoral College is a body of electors chosen by the voters in each state to elect the President and Vice President of the United States. The number of electors from each state is equal to the number of senators and representatives that state has in Congress.
Purpose and Structure
- To elect the President and Vice President
- Each state has a number of electors equal to its number of senators and representatives in Congress
- Electors are chosen by the voters in each state
The Electoral College has been criticized for giving too much power to small states and for not always reflecting the popular vote. However, it is a unique feature of the American political system that has been in place since the founding of the nation.
Bill of Rights: Match The Appropriate Constitutional Convention Plan With Its Features.
The Bill of Rights is the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. It was adopted in 1791 to protect the rights of individuals from government overreach.
Key Provisions
- Freedom of speech, press, religion, and assembly
- Right to bear arms
- Protection against unreasonable searches and seizures
- Right to a fair trial
- Right to due process of law
The Bill of Rights is a cornerstone of American democracy and has played a vital role in protecting the rights of individuals.
User Queries
What was the main difference between the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan?
The Virginia Plan proposed a bicameral legislature with representation based on population, while the New Jersey Plan proposed a unicameral legislature with equal representation for each state.
How did the Connecticut Compromise resolve the conflict between the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan?
The Connecticut Compromise created a bicameral legislature with the Senate representing states equally and the House of Representatives representing states based on population.
What was the purpose of the Three-Fifths Compromise?
The Three-Fifths Compromise counted enslaved people as three-fifths of a free person for the purposes of representation and taxation.