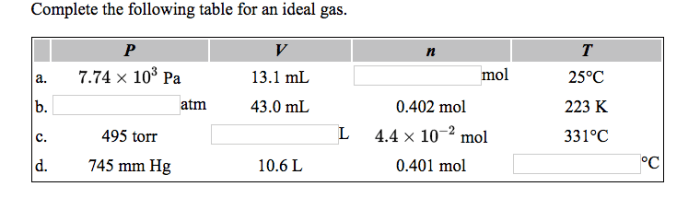
Complete the following table for an ideal gas – Complete the table for an ideal gas is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the behavior of gases under various conditions. It involves understanding the relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles in an ideal gas.
This comprehensive guide delves into the properties of ideal gases, exploring Boyle’s Law, Charles’s Law, Gay-Lussac’s Law, the Combined Gas Law, and Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures. Through examples and applications, we will gain a deeper understanding of gas behavior and its significance in various scientific and engineering fields.
Ideal Gas Properties
An ideal gas is a hypothetical gas that follows the ideal gas law under all conditions. The ideal gas law is a mathematical equation that describes the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of a gas.
It is given by the equation PV = nRT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the temperature.
The ideal gas law can be used to predict the behavior of real gases under a wide range of conditions. However, real gases only behave like ideal gases under certain conditions. For example, real gases deviate from ideal behavior at high pressures and low temperatures.
Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume. In other words, as the volume of a gas increases, its pressure decreases, and as the volume of a gas decreases, its pressure increases.
Boyle’s Law can be used to explain a variety of phenomena, such as the behavior of a balloon as it is inflated and deflated. As the balloon is inflated, its volume increases and its pressure decreases. As the balloon is deflated, its volume decreases and its pressure increases.
Charles’s Law
Charles’s Law describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure. It states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature. In other words, as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume increases, and as the temperature of a gas decreases, its volume decreases.
Charles’s Law can be used to explain a variety of phenomena, such as the behavior of a hot air balloon. As the hot air balloon is heated, its temperature increases and its volume increases. This causes the balloon to rise.
Gay-Lussac’s Law
Gay-Lussac’s Law describes the relationship between the pressure and temperature of a gas at constant volume. It states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature. In other words, as the temperature of a gas increases, its pressure increases, and as the temperature of a gas decreases, its pressure decreases.
Gay-Lussac’s Law can be used to explain a variety of phenomena, such as the behavior of a pressure cooker. As the pressure cooker is heated, its temperature increases and its pressure increases. This causes the food inside the pressure cooker to cook faster.
Combined Gas Law, Complete the following table for an ideal gas
The Combined Gas Law combines Boyle’s Law, Charles’s Law, and Gay-Lussac’s Law into a single equation. The Combined Gas Law states that the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas are all related to each other. The Combined Gas Law can be used to predict the behavior of a gas under a variety of conditions.
The Combined Gas Law can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as predicting the pressure of a gas in a container when the volume and temperature of the gas are changed.
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture. The partial pressure of a gas is the pressure that the gas would exert if it were the only gas in the container.
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures can be used to explain a variety of phenomena, such as the behavior of a scuba diver. As a scuba diver descends deeper into the water, the pressure of the water increases. This causes the partial pressure of the nitrogen in the diver’s lungs to increase.
This can lead to nitrogen narcosis, which is a condition that can cause dizziness, confusion, and even unconsciousness.
Helpful Answers: Complete The Following Table For An Ideal Gas
What is an ideal gas?
An ideal gas is a hypothetical gas that obeys the gas laws perfectly. It consists of point particles with no intermolecular forces and occupies no volume.
What is the Combined Gas Law?
The Combined Gas Law combines Boyle’s Law, Charles’s Law, and Gay-Lussac’s Law into a single equation that relates pressure, volume, temperature, and moles for an ideal gas under different conditions.